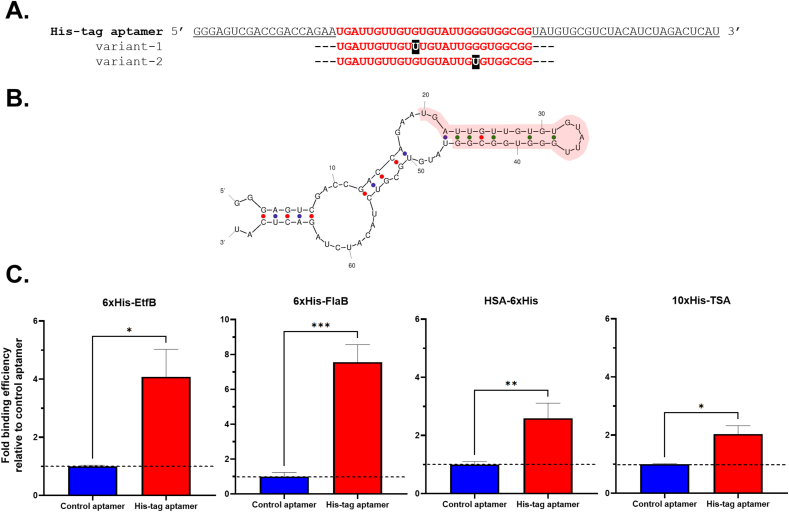
Abstract
The polyhistidine (His) tag is one of the most widely used tags for protein expression, detection, and purification. Aptamers targeting the His tag have been developed for various applications, including western blotting, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation, due to their advantages over His-tag antibodies. However, previously reported His-tag aptamers are either DNA or unmodified RNA, both of which are susceptible to nuclease degradation, limiting their stability. In this study, we report a modified RNA aptamer that specifically recognizes the His tag. This aptamer incorporates 2′-fluoropyrimidine substitutions in its pyrimidine nucleotides, enhancing its resistance to nuclease degradation. It specifically binds to His tags consisting of six or more histidine residues located at either the amino or carboxyl terminus of a protein. Furthermore, the aptamer was successfully utilized for the quantification of His-tagged proteins using an electrochemical aptasensor-based detection system, achieving a linear detection range of 50-300 nM. Thus, this novel His-tag-binding RNA aptamer holds significant potential for various applications. Moreover, its compatibility with other therapeutic or diagnostic 2′-fluoropyrimidine RNA aptamers can facilitate the generation of bispecific RNA molecules, thereby expanding its utility.