RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
Multi-Pass Arrival Time Correction in Cyclic Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry for Imaging and Shotgun Lipidomics
Abstract Direct-infusion mass spectrometry (DI-MS) and mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) are powerful techniques for lipidomics research. However, annotating isomeric and isobaric lipids with these methods is challenging due to the absence of chromatographic separation. Recently, cyclic ion mobility mass spectrometry (cIM-MS) has been proposed to overcome this limitation. However, fluctuations in room conditions can affect ion mobility multipass arrival times, [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Disproportionately Increasing Incidence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Female Patients and the Elderly: An Update Analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021
Abstract Introduction: To update the global burden of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) using data from the Global Burden of Disease 2021. Methods: Data from Global Burden of Disease 2021 were analyzed to assess the IBD burden. Results: In 2021, there were 375,140 new cases and 3.83 million total cases of IBD. Elderly onset IBD accounted for 11% of incidences. 167 [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมSingle-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral blood links cell-type-specific regulation of splicing to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases
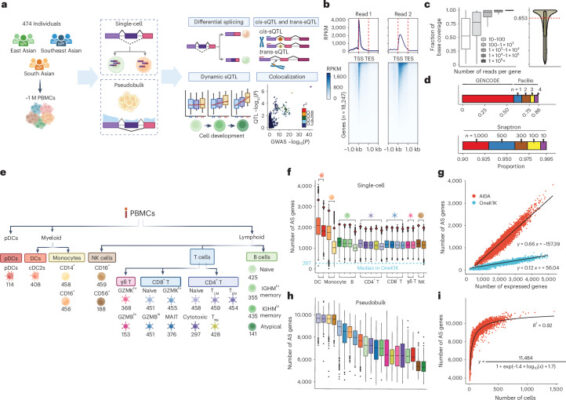
Abstract Alternative splicing contributes to complex traits, but whether this differs in trait-relevant cell types across diverse genetic ancestries is unclear. Here we describe cell-type-specific, sex-biased and ancestry-biased alternative splicing in ~1 M peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 474 healthy donors from the Asian Immune Diversity Atlas. We identify widespread sex-biased and ancestry-biased differential splicing, most of which is cell-type-specific. [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Cold-pressed extraction of perilla seed oil enriched with alpha-linolenic acid mitigates tumour progression and restores gut microbial homeostasis in the AOM/DSS mice model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer
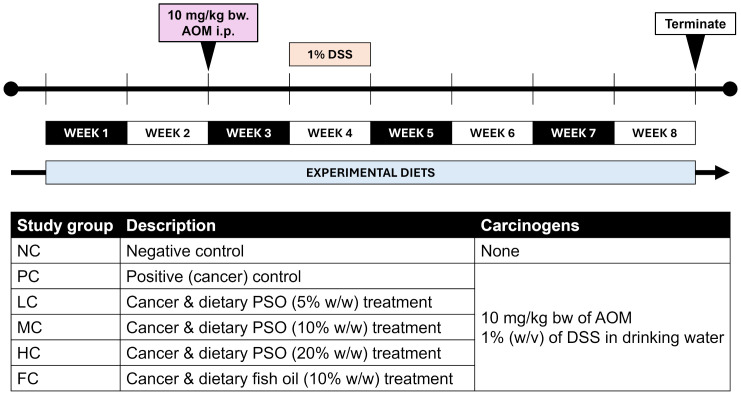
Abstract The present investigation explores into the influence of dietary nutrients, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-derived omega-3 fatty acid abundant in perilla seed oil (PSO), on the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CRC). The study employs a mouse model to scrutinize the effects of ALA-rich PSO in the context of inflammation-driven CRC. Perilla seeds were subjected to oil extraction, [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Metabolic and genetic risk factors associated with pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes in Thai healthcare employees: A long-term study from the Siriraj Health (SIH) cohort study
Abstract Background The study of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in a developing country like Thailand has rarely been conducted in long-term cohorts, especially among the working-age population. We aim to assess the prevalence and incidence of risk factors and their associations underlying NCDs, especially type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) among healthcare workers enrolled in the Siriraj Health (SIH) study cohort. Methods The [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมCAIM: coverage-based analysis for identification of microbiome
Abstract Accurate taxonomic profiling of microbial taxa in a metagenomic sample is vital to gain insights into microbial ecology. Recent advancements in sequencing technologies have contributed tremendously toward understanding these microbes at species resolution through a whole shotgun metagenomic approach. In this study, we developed a new bioinformatics tool, coverage-based analysis for identification of microbiome (CAIM), for accurate taxonomic classification [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมIs Exon Skipping a Viable Therapeutic Approach for Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome with Mutations in COL3A1 Exon 10 or 15?
Abstract Vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndrome or Ehlers–Danlos syndrome type IV (vEDS) is a connective tissue disorder characterised by skin hyperextensibility, joint hypermobility and fatal vascular rupture caused by COL3A1 mutations that affect collagen III expression, homo-trimer assembly and secretion. Along with collagens I, II, V and XI, collagen III plays an important role in the extracellular matrix, particularly in the inner [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมGLIMMERS: glioma molecular markers exploration using long-read sequencing
Abstract The revised WHO guidelines for classifying and grading brain tumors include several copy number variation (CNV) markers. The turnaround time for detecting CNVs and alterations throughout the entire genome is drastically reduced with the customized read incremental approach on the nanopore platform. However, this approach is challenging for non-bioinformaticians due to the need to use multiple software tools, extract [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมEpigallocatechin Gallate Potentiates the Anticancer Effect of AFP-siRNA-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
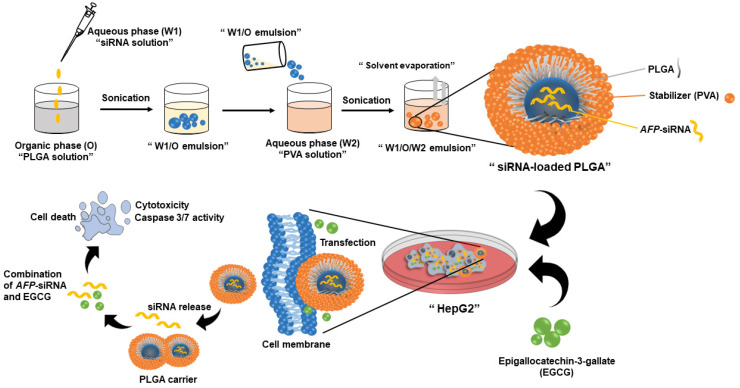
Abstract To develop a potential cancer treatment, we formulated a novel drug delivery platform made of poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) and used a combination of an emerging siRNA technology and an extracted natural substance called catechins. The synthesized materials were characterized to determine their properties, including morphology, hydrodynamic size, charge, particle stability, and drug release profile. The therapeutic effect of AFP-siRNA [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
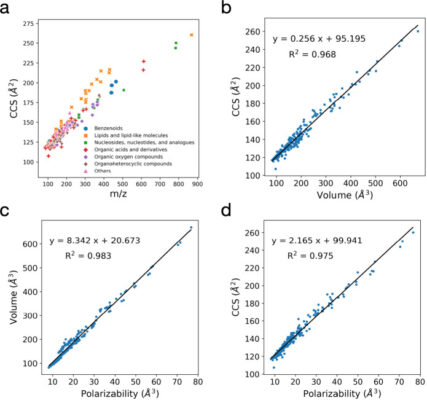
Accurate Prediction of Ion Mobility Collision Cross-Section Using Ion’s Polarizability and Molecular Mass with Limited Data
Abstract The rotationally averaged collision cross-section (CCS) determined by ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS) facilitates the identification of various biomolecules. Although machine learning (ML) models have recently emerged as a highly accurate approach for predicting CCS values, they rely on large data sets from various instruments, calibrants, and setups, which can introduce additional errors. In this study, we identified and validated [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
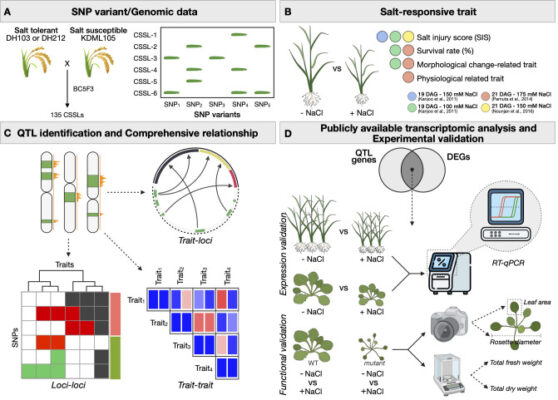
Comparative quantitative trait loci analysis framework reveals relationships between salt stress responsive phenotypes and pathways
Abstract Soil salinity is a complex abiotic stress that involves several biological pathways. Hence, focusing on a specific or a few salt-tolerant phenotypes is unlikely to provide comprehensive insights into the intricate and interwinding mechanisms that regulate salt responsiveness. In this study, we develop a heuristic framework for systematically integrating and comprehensively evaluating quantitative trait loci (QTL) analyses from multiple [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
A Precision Therapy Approach for Retinitis Pigmentosa 11 Using Splice-Switching Antisense Oligonucleotides to Restore the Open Reading Frame of PRPF31
Abstract Retinitis pigmentosa 11 is an untreatable, dominantly inherited retinal disease caused by heterozygous mutations in pre-mRNA processing factor 31 PRPF31. The expression level of PRPF31 is linked to incomplete penetrance in affected families; mutation carriers with higher PRPF31 expression can remain asymptomatic. The current study explores an antisense oligonucleotide exon skipping strategy to treat RP11 caused by truncating mutations [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมData processing solutions to render metabolomics more quantitative: case studies in food and clinical metabolomics using Metabox 2.0
Abstract In classic semiquantitative metabolomics, metabolite intensities are affected by biological factors and other unwanted variations. A systematic evaluation of the data processing methods is crucial to identify adequate processing procedures for a given experimental setup. Current comparative studies are mostly focused on peak area data but not on absolute concentrations. In this study, we evaluated data processing methods to [...]
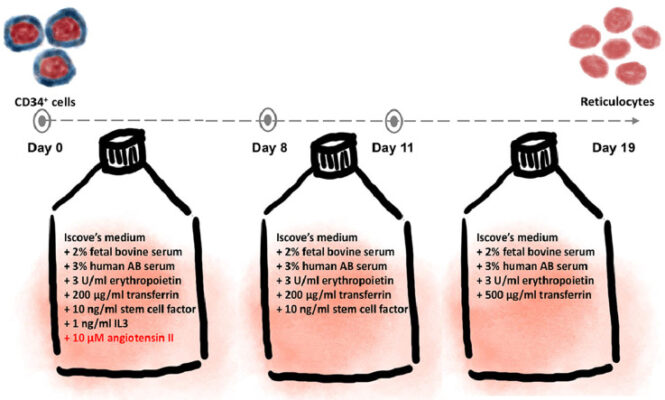
อ่านเพิ่มเติมAngiotensin II promotes erythroid proliferation in a three-stage erythroid culture system
Abstract At present, the numbers of cultured erythroid cells obtained from culture systems are not on a scale that can be used for therapeutics since the cultured erythroid cells have limited proliferation capacity. Stromal cells are believed to play important roles during erythropoiesis. Our previous study shows that factors secreted by stromal cells enhance the proliferation capacity of adult erythroid [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
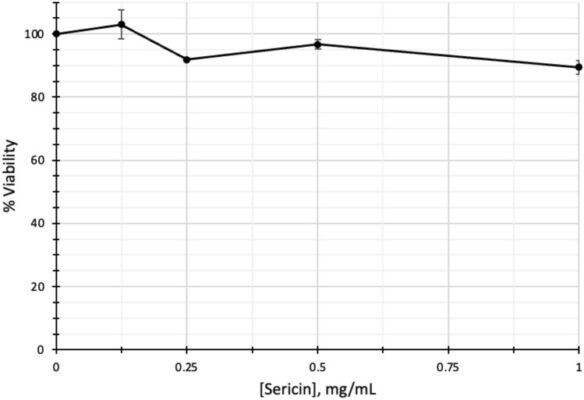
Transcriptomic screening of novel targets of sericin in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract Sericin, a natural protein derived from Bombyx mori, is known to ameliorate liver tissue damage; however, its molecular mechanism remains unclear. Herein, we aimed to identify the possible novel targets of sericin in hepatocytes and related cellular pathways. RNA sequencing analysis indicated that a low dose of sericin resulted in 18 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) being upregulated and 68 [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
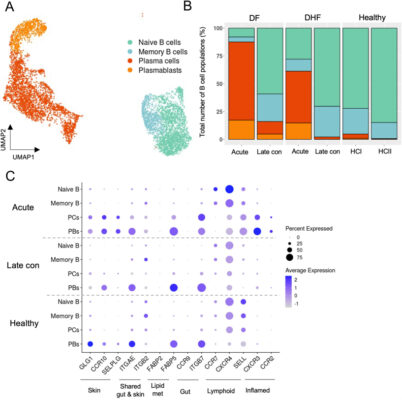
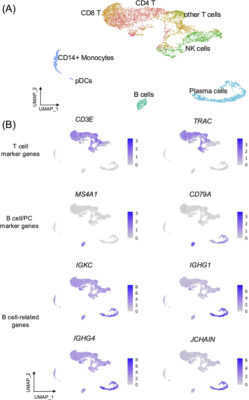
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the expansion of circulating tissue-homing B cell subsets in secondary acute dengue viral infection
Abstract The roles of antibodies secreted by subsets of B cells in dengue virus (DENV) infection have been extensively studied, yet, the contribution of tissue-homing B cells to antiviral immunity remains unclear. In this study, we performed a comprehensive analysis of B cell subpopulations in peripheral blood samples from DENV-infected patients using single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets and flow cytometry. We [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
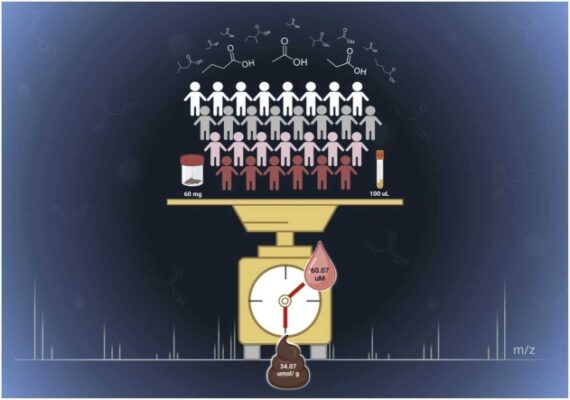
Quantifying fecal and plasma short-chain fatty acids in healthy Thai individuals
Abstract Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are involved in important physiological processes such as gut health and immune response, and changes in SCFA levels can be indicative of disease. Despite the importance of SCFAs in human health and disease, reference values for fecal and plasma SCFA concentrations in healthy individuals are scarce. To address this gap in current knowledge, we developed [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
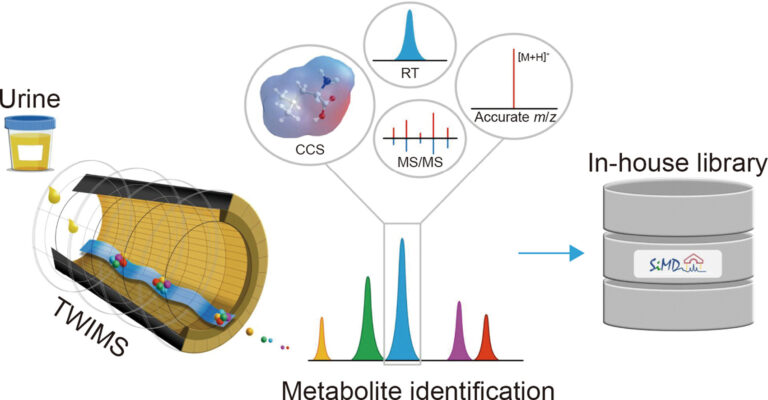
Measurement of very low-molecular weight metabolites by traveling wave ion mobility and its use in human urine samples
Abstract The collision cross-sections (CCS) measurement using ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) in combination with mass spectrometry (MS) offers a great opportunity to increase confidence in metabolite identification. However, owing to the lack of sensitivity and resolution, IMS has an analytical challenge in studying the CCS values of very low-molecular-weight metabolites (VLMs ≤ 250 Da). Here, we describe an analytical method [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Identification of RNF213 as a Potential Suppressor of Local Invasion in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is a lethal cancer with poor survival especially when it spreads. The histopathology of its rare intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct type (IPNB) characteristically shows cancer cells originating within the confined bile duct space. These cells eventually invade and infiltrate the nearby liver tissues, making it a good model to study the mechanism of [...]
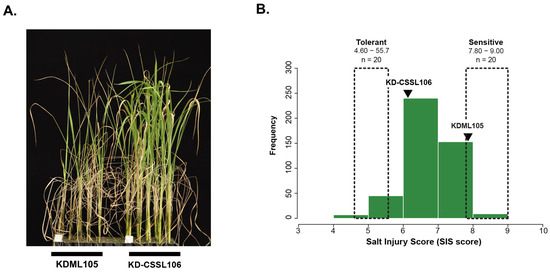
อ่านเพิ่มเติมIdentification of Candidate Genes for Salt Tolerance at Seedling Stage in Rice Using QTL-Seq and Chromosome Segment Substitution Line-Derived Population
Abstract Rice is a staple food for more than half of the world’s population. However, the pervasive problem of salinity is severely undermining rice production, especially in coastal and low-lying areas where soil salinization is widespread. This stress, exacerbated by climate change, necessitates the development of salt-tolerant rice varieties to ensure food security. In this study, an F2:3 population (n [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Discovery of procyanidin condensed tannins of (-)-epicatechin from Kratom, Mitragyna speciosa, as virucidal agents against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract Kratom, Mitragyna speciosa, is one of the most popular herbs in the West and Southeast Asia. A number of previous works have focused on bioactive alkaloids in this plant; however, non-alkaloids have never been investigated for their biological activities. Antiviral and virucidal assays of a methanol leaf extract of Kratom, M. speciosa, revealed that a crude extract displayed virucidal [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมInvestigating common mutations in ATP7B gene and the prevalence of Wilson’s disease in the Thai population using population-based genome-wide datasets
Abstract Wilson’s disease (WD) is a rare metabolic disorder caused by variations in the ATP7B gene. It usually manifests hepatic, neurologic, and psychiatric symptoms due to excessive copper accumulation. The prevalence of WD and its common variants differ across populations. This study aimed to examine these aspects of WD within the Thai population, where information has been limited. We reviewed [...]
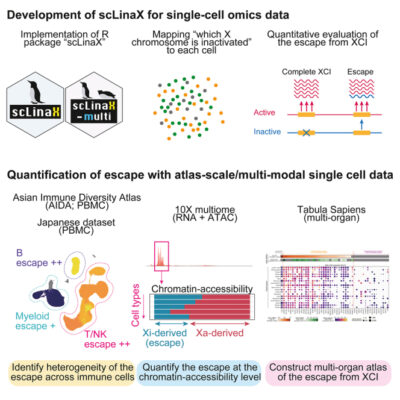
อ่านเพิ่มเติมQuantification of escape from X chromosome inactivation with single-cell omics data reveals heterogeneity across cell types and tissues
Abstract Several X-linked genes escape from X chromosome inactivation (XCI), while differences in escape across cell types and tissues are still poorly characterized. Here, we developed scLinaX for directly quantifying relative gene expression from the inactivated X chromosome with droplet-based single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data. The scLinaX and differentially expressed gene analyses with large-scale blood scRNA-seq datasets consistently identified the [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
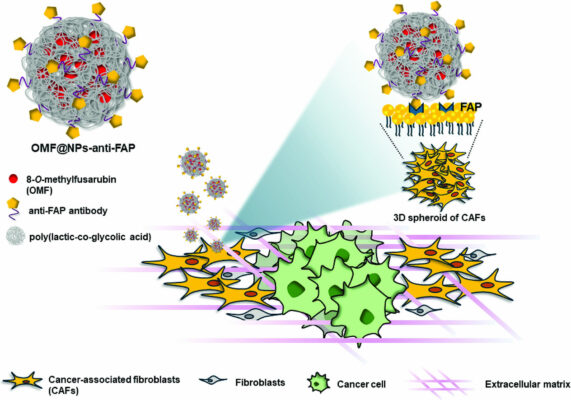
Development of cancer-associated fibroblasts-targeting polymeric nanoparticles loaded with 8-O-methylfusarubin for breast cancer treatment
Abstract Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are abundant stromal cells residing in a tumor microenvironment (TME) which are associated with the progression of tumor. Herein, we developed novel CAFs-targeting polymeric nanoparticles encapsulating a synthetic 8-O-methylfusarubin (OMF) compound (OMF@NPs-anti-FAP). Anti-FAP/fibroblast activation protein antibody was employed as a CAFs-targeting ligand. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized nanomaterials were firstly investigated with various techniques. The [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
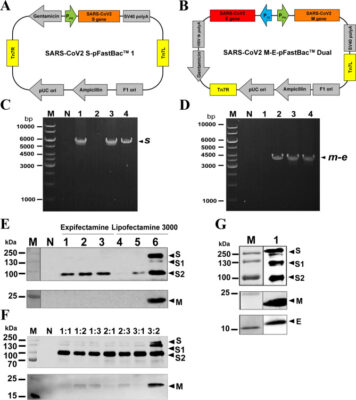
Immunogenicity of intraperitoneal and intranasal liposome adjuvanted VLP vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract Humans get SARS-CoV-2 infection mainly through inhalation; thus, vaccine that induces protective immunity at the virus entry site is important for early control of the infection. In this study, two anionic liposome (L)-adjuvanted VLP vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 were formulated. Baculovirus-Sf21 insect cell system was used for production of VLPs made of full-length S, M and E proteins. S protein [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
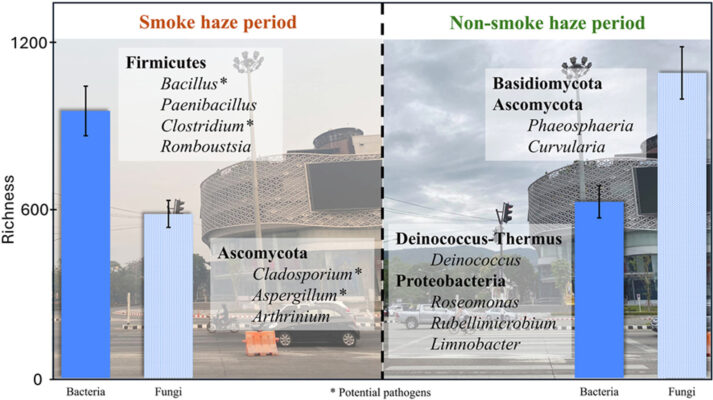
Characterization of airborne microbial communities in northern Thailand: Impacts of smoke haze versus non-haze conditions
Abstract Data on airborne microorganisms, particularly in Southeast Asia, are more limited compared to chemical data. This study is the first to examine the community and diversity of microorganisms on PM2.5 in an urban area of Northern Thailand during both smoke haze and non-smoke haze periods of 2020. This study evaluated the composition of airborne bacteria and fungi and analyzed [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
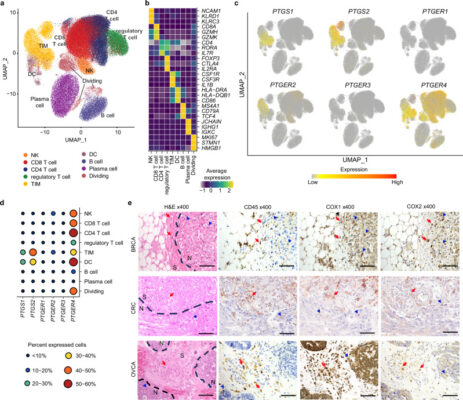
Prostaglandin E2-EP2/EP4 signaling induces immunosuppression in human cancer by impairing bioenergetics and ribosome biogenesis in immune cells
Abstract While prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is produced in human tumor microenvironment (TME), its role therein remains poorly understood. Here, we examine this issue by comparative single-cell RNA sequencing of immune cells infiltrating human cancers and syngeneic tumors in female mice. PGE receptors EP4 and EP2 are expressed in lymphocytes and myeloid cells, and their expression is associated with the downregulation [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
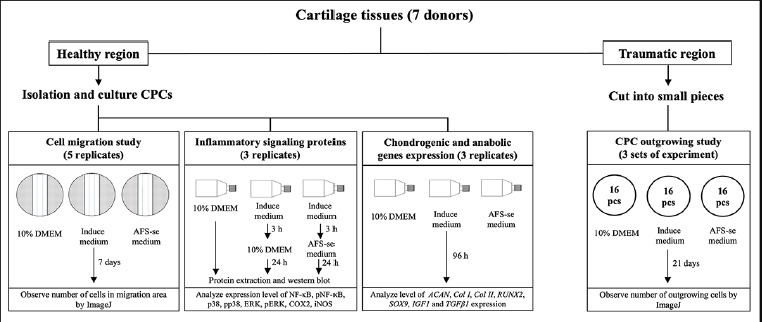
MSC secretome from amniotic fluid halts IL-1β and TNF-α inflammation via the ERK/MAPK pathway, promoting cartilage regeneration in OA in vitro
Abstract Summary Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative disease that causes chronic pain and disability worldwide. This disease is mainly caused by IL-1β and TNF-α, which lead to cartilage degradation and inhibit the repair capacity of damaged cartilage. Recent studies have shown that amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells (AF-MSCs) secrete proteins that can effectively help in the treatment of cartilage damaged [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
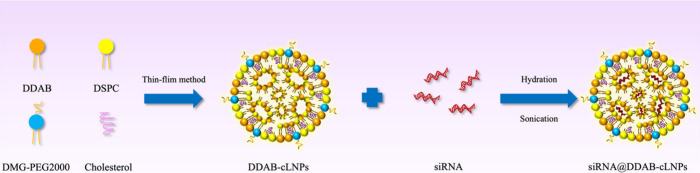
Development of Small Interfering RNA Loaded Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Liver Cancer with Elevated α-Fetoprotein Expression
Abstract α-Fetoprotein (AFP) is an oncogenic glycoprotein that is overexpressed in most patients with liver cancer. Moreover, it significantly affects tumorigenesis and progression, particularly by inhibiting programmed cell death or apoptosis. The treatment of liver cancer with chemotherapy is currently still in use, but its toxicity is a major concern. Alternatively, targeted therapy, especially small interfering RNA (siRNA)-based therapeutics that [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
In vitro comparison of cerumenolytic efficacy: 2.5 % sodium bicarbonate versus 0.5 % sodium docusate based on cerumen weight gain
Abstract Objective: This study aimed to compare the cerumenolytic efficacy of 2.5 % sodium bicarbonate prepared in-house with that of commercially available 0.5 % sodium docusate, utilizing cerumen weight gain and disintegration degree as metrics. Methods: Cerumen samples were collected from patients at an otorhinolaryngology outpatient clinic at a tertiary care hospital. This study evaluated the differences in cerumen weight [...]
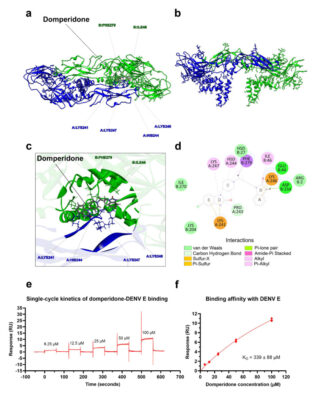
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDomperidone inhibits dengue virus infection by targeting the viral envelope protein and nonstructural protein 1
Abstract Dengue is a mosquito-borne disease caused by dengue virus (DENV) infection, which remains a major public health concern worldwide owing to the lack of specific treatments or antiviral drugs available. This study investigated the potential repurposing of domperidone, an antiemetic and gastrokinetic agent, to control DENV infection. Domperidone was identified by pharmacophore-based virtual screening as a small molecule that [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
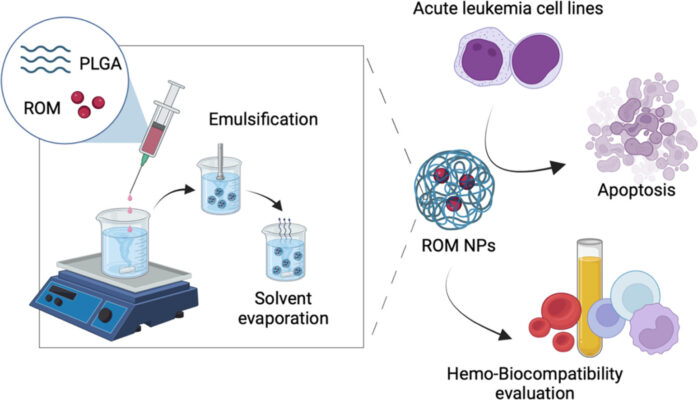
Enhancement of the in vitro anti-leukemic effect of the histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin using Poly-(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles as a drug carrier
Abstract The goal of this work is to develop a delivery system for histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi) romidepsin (ROM) using Poly(D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) as a carrier and evaluate its anti-leukemic effects. Romidepsin-loaded nanoparticles (ROM NPs) required for this purpose were fabricated using a single emulsion-solvent evaporation technique. Their physical characteristics and in vitro drug release profiles were studied, alongside biocompatibility and [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Production of recombinant electron transfer flavoprotein beta subunit protein and its application in a lateral flow assay for early diagnosis of leptospirosis
Abstract Leptospirosis is a major cause of acute febrile illness, often presenting with non-specific symptoms that can lead to misdiagnosis. Early laboratory diagnosis is essential for confirmation to avoid misdiagnosis and ensure appropriate management. This study aimed to identify and produce a recombinant protein, approximately 25 kDa, with high antigenicity for diagnostic applications. The 25 kDa protein from Leptospira interrogans [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมEfficacy, Safety, and Cost-effectiveness of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Whitfield’s Spirit Solution for Treating Superficial Fungal Foot Infections: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract Introduction: A novel antifungal formulation combining zinc oxide nanoparticles and Whitfield’s spirit solution (ZnO-WFs) was developed to enhance the treatment of superficial fungal foot infections. Methods: This 8-week, randomized, double-blinded controlled trial compared the efficacy, safety, and cost-effectiveness of ZnO-WFs with those of Whitfield’s spirit solution (WFs) alone and a zinc oxide nanoparticle solution (ZnOs). Seventy of the 84 [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Enhanced Anticancer Effects Through Combined Therapeutic Model of Macrophage Polarization and Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Multifunctional Lipid Nanocomposites
Abstract Although the mono-anticancer therapy approach particularly directly targeting tumors is still common, this conventional method is generally deemed not effective and insufficient. In tumor microenvironment (TME), tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs, referred to as M2-polarized) play a crucial role in creating an immunosuppressive TME, contributing to various pro-tumorigenic effects. A promising strategy to inhibit tumor growth involves re-educating M2 macrophages into [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมAsian diversity in human immune cells
Abstract The relationships of human diversity with biomedical phenotypes are pervasive yet remain understudied, particularly in a single-cell genomics context. Here, we present the Asian Immune Diversity Atlas (AIDA), a multi-national single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) healthy reference atlas of human immune cells. AIDA comprises 1,265,624 circulating immune cells from 619 donors, spanning 7 population groups across 5 Asian countries, and [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมInvestigation of southern Thailand sweet pickled mango metabolic profiles related to deterioration
Abstract Southern Thailand sweet pickled mango (MBC) is a famous delicacy and economically important for the local communities. This study aimed to elucidate important metabolites related to MBC deterioration at 4 °C (STR4) and 30 °C (STR30). The results show that deterioration of MBCs was linked to increased levels of ethyl acetate, isopropyl alcohol, trans-β-ocimene, isopentyl acetate, 2-phenethyl acetate, glucose, [...]
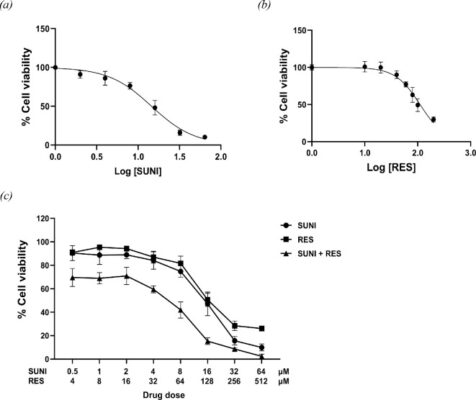
อ่านเพิ่มเติมSynergistic anticancer activity of resveratrol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles and sunitinib in colorectal cancer treatment
Abstract The development of novel and effective treatment strategies, particularly through drug combinations, can significantly enhance therapeutic outcomes. This study explores the innovative combination of resveratrol (RES), a phenolic compound, with sunitinib (SUNI), a multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for targeting human colon adenocarcinoma cell line HT-29. We identified a synergistic effect at a SUNI:RES ratio of 1:8, based on their [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
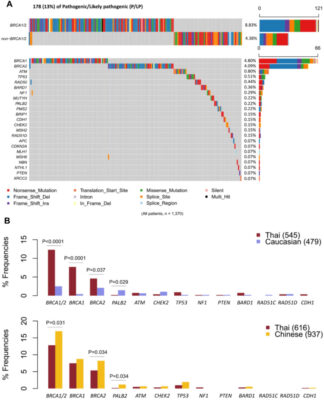
Comprehensive germline and somatic profiling of high-risk Thai breast cancer via next-generation sequencing
Abstract Breast cancer genomic landscapes differ across ethnic groups, yet the somatic profile of Thai breast tumours has remained uncharacterised. This study analysed 1676 high-hereditary-risk Thai breast cancer patients, identified according to National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guideline. Germline alterations were assessed in 1370 cases using a custom 36-core cancer panel. Somatic mutations were characterised in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumour tissues [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Genomic Assessment, Metabolic Profile Mapping, and Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity of Lactococcus lactis SK2-659 from Thai Fermented Green Mustard (Pak-kad-dong)
Abstract Probiotics play crucial roles in promoting gut health, enhancing immunity, and combating pathogenic microorganisms, with increasing interest in their applications in the food and therapeutic industries. Lactococcus lactis, a well-known lactic acid bacterium, has emerged as a promising candidate owing to its probiotic traits and safety profile. In this study, we investigated the probiotic potential and genomic profile of [...]
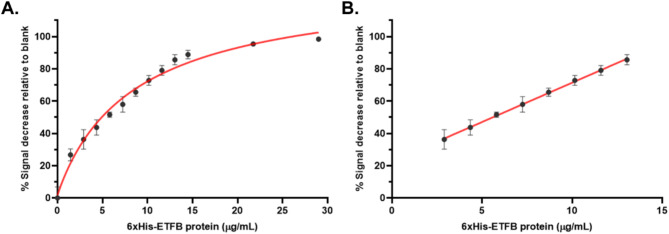
อ่านเพิ่มเติมPerformance of electrochemical aptasensor as antigen test in clinical samples for early diagnosis of leptospirosis
Abstract Early diagnosis of leptospirosis is critical for timely treatment and effective disease management. This study evaluated the diagnostic performance of a novel electrochemical aptasensor targeting the electron transfer flavoprotein subunit beta (EtfB) of Leptospira interrogans in clinical samples collected during the acute phase of leptospirosis. The aptasensor assay was tested using plasma samples and compared to the microscopic agglutination [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
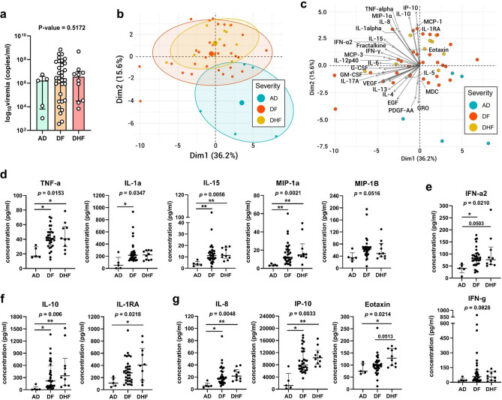
Cytokine and chemokine kinetics in natural human dengue infection as predictors of disease outcome
Abstract Dengue is an important tropical disease with considerable global impact. Despite this, there remains an urgent need for reliable biomarkers to predict disease severity, as well as effective antiviral drugs and targeted treatments. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive profiling of 41 plasma mediators in patients with asymptomatic dengue (AD) and symptomatic dengue (SD), which includes mild dengue [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
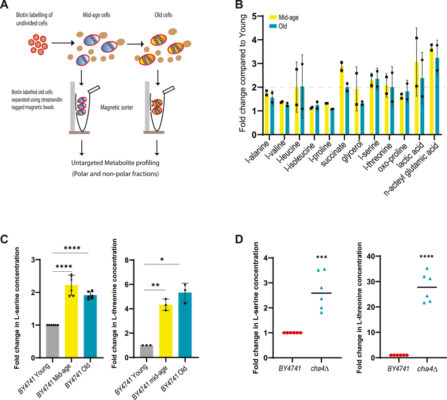
Perturbations in L-serine metabolism regulate protein quality control through the sensor of the retrograde response pathway RTG2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract Cellular protein homeostasis relies on a complex network of protein synthesis, folding, sub-cellular localization, and degradation to sustain a functional proteome. Since most of these processes are energy-driven, proteostasis is inescapably afflicted by cellular metabolism. Proteostasis collapse and metabolic imbalance are both linked to aging and age-associated disorders, yet they have traditionally been studied as separate phenomena in the [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
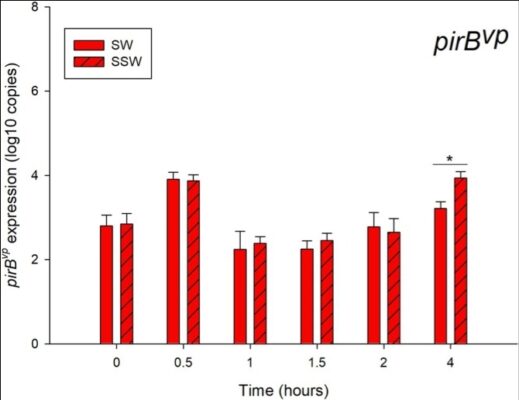
Pathogenic Characteristics of Shrimp Early Mortality Syndrome (EMS)-Causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus: A Comparative Transcriptomic Study Suggests the Relationship Between Metabolic Fitness and Virulence Gene Expression
Abstract Vibrio parahaemolyticus (VP) is a major bacterial species that causes early mortality syndrome (EMS) in shrimps. EMS can be classified into two groups based on histological signs of hepatopancreatic tissues, i.e., acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) and non-AHPND. To investigate how toxin-producing AHPND and toxin-lacking non-AHPND VP could lead to EMS, growth characteristics and transcriptomic analyses of the representative [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมFeb
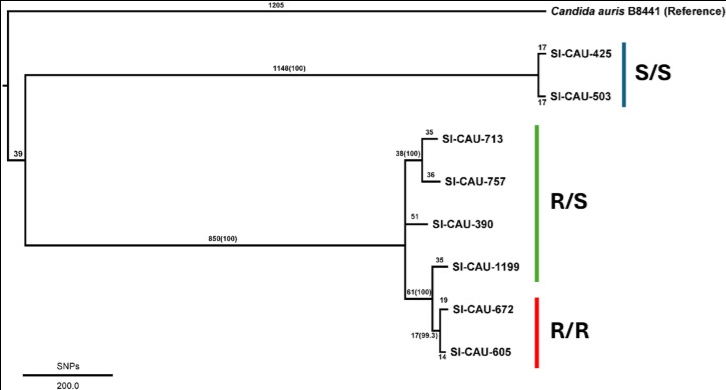
A study of genomic complexity underlying multidrug resistance in Candida auris strains in Thailand
Abstract Candida auris, one of the emerging multidrug-resistant Candida species, was first discovered in 2009 from the ear canal of a patient in Tokyo, Japan. Since then, several studies exhibit the possible threats of C. auris due to its versatile resistance to frontline antifungal agents. The number of studies focusing on genetic variants associated with multidrug resistance has risen over [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมJan
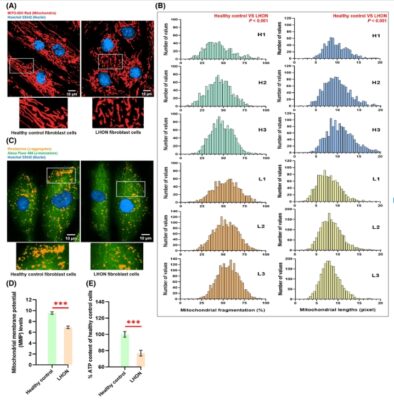
Metformin promotes mitochondrial integrity through AMPK‐signaling in Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy
Abstract Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a maternally inherited disorder caused by mitochondrial DNA mutations in complex I of the respiratory chain, leading to impaired ATP production, mitochondrial fragmentation, and oxidative stress that contribute to vision loss. This study investigated the potential repurposing of metformin, a widely used antidiabetic drug, in fibroblasts from LHON patients carrying the m.11778G>A mutation. [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมJan
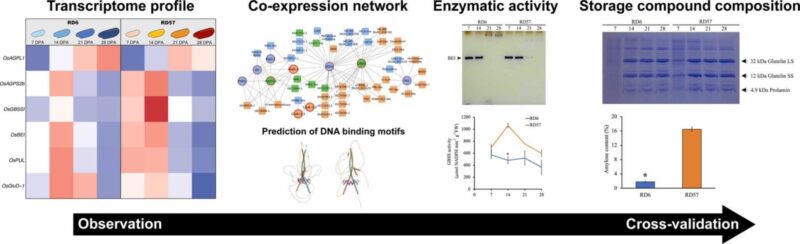
Unveiling distinct storage composition and starch properties in developing indica rice grains via transcriptional profiling and enzymatic activity analysis
Abstract The starch and protein in rice grains determine their nutritional value, eating and cooking quality (ECQ), and potential applications as a biopolymer. Building on previously identified functional differences between two Thai indica cultivars, waxy RD6 and high-amylose RD57, we examined the transcriptional regulation of their storage polymers by profiling key starch-biosynthetic and storage-protein genes in developing endosperms at 7-, [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมJan
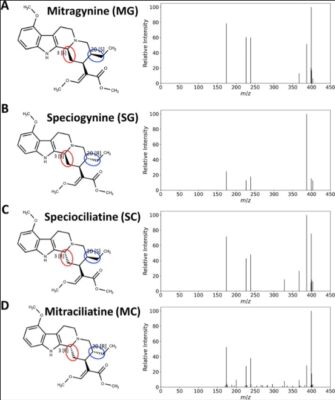
Spatial Mapping of Stereoisomeric and Isobaric Alkaloids in Mitragyna speciosa Tissues by High-Resolution DESI-cIM-MS
Abstract Conventional mass spectrometry imaging (MSI), even when combined with low-resolution ion mobility, lacks the resolving power to distinguish stereoisomers. To address this limitation, we developed a high-resolution desorption electrospray ionization cyclic ion mobility mass spectrometry (DESI-cIM-MS) method for in situ separation and spatial mapping of stereoisomeric compounds, using Mitragyna speciosa (kratom) as a model system. We characterized and validated [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมJan
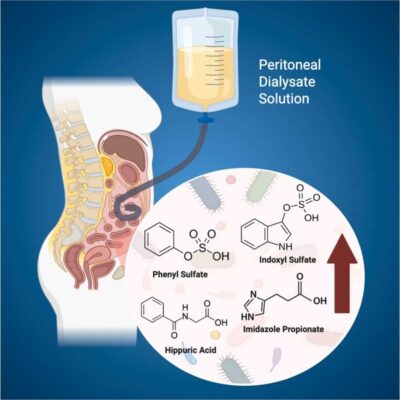
LC-MS/MS identifies elevated imidazole propionate and gut-derived metabolite alterations in peritoneal dialysis patients
Abstract We developed a robust LC–MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 16 uremic toxins (UTs) and 14 bile acids (BAs) in plasma and fecal samples within a single method. The method demonstrated high sensitivity, broad metabolite coverage, and excellent accuracy, precision, and throughput. Using this platform, targeted metabolites were quantified in peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients (n = 31) and healthy controls [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมJan
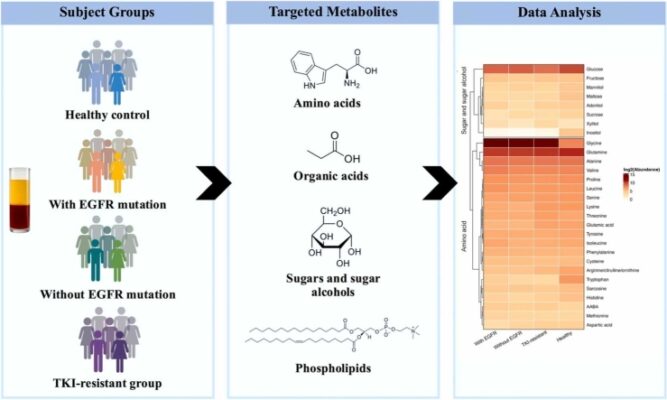
Plasma metabolomic analysis in Thai EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients
Abstract Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, underscoring the urgent need for non-invasive approaches to improve diagnosis, patient stratification, and therapeutic monitoring. Metabolic reprogramming driven by oncogenic alterations-particularly Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)-creates distinctive plasma signatures with clinical relevance. In this study, plasma metabolomic profiling revealed that amino acid [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
Understanding and mitigating the impact of ambient mRNA contamination in single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis
Abstract Droplet-based single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) frequently encounters significant challenges from contamination of cell-free mRNAs, known as “ambient mRNAs”, which can substantially distort single-cell transcriptome data interpretation to a large extent. In this study, we investigate the impact of ambient mRNA contamination on differential gene expression and biological pathway enrichment analyses, using two independent scRNA-seq datasets: ten peripheral blood mononuclear [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
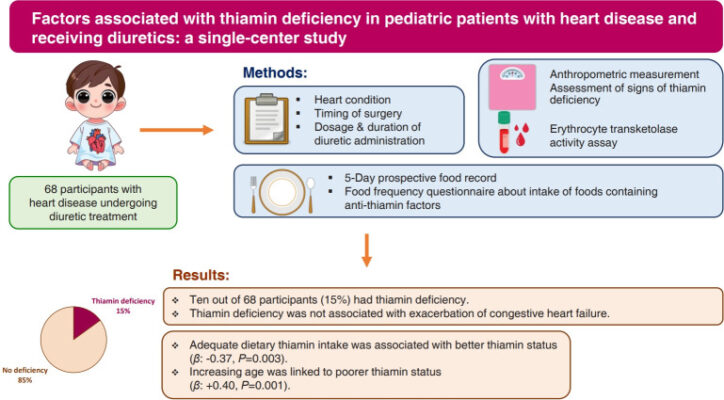
Factors associated with thiamin deficiency in pediatric patients with heart disease and receiving diuretics: a single-center study
Abstract Background: Thiamin deficiency (TD) manifesting clinically as wet beriberi can significantly impair a patient’s cardiac function. Children with heart disease who are receiving diuretic treatment may be at increased risk for severe clinical manifestations of TD. Purpose: This study aimed to determine the prevalence of TD and evaluate the association between various factors with thiamin status in pediatric patients [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมDec
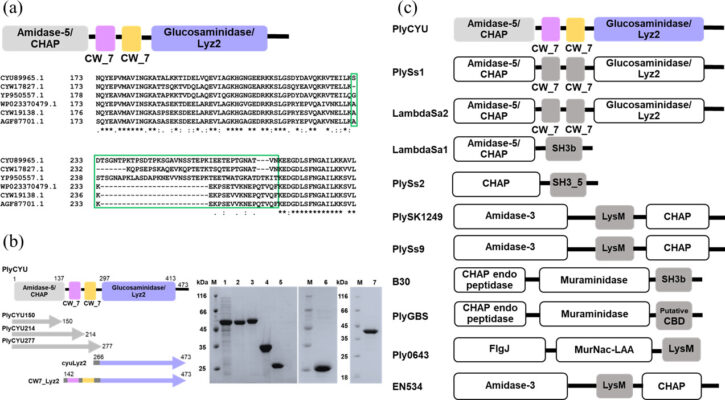
PlyCYU endolysin targeting Streptococcus agalactiae exhibits a CHAP activity and a glucosaminidase domain mediating multimerization
Abstract Bacteriophage endolysins are attractive alternatives to antibiotics owing to their rapid action, host specificity, and unlikeliness of resistance development. Here, bioinformatic analysis of Streptococcus suis prophage sequences identified an endolysin, named PlyCYU, containing two putative catalytic domains-an N-terminal amidase_5 and a C-terminal glucosaminidase (Lyz2) domain-with two CW_7 family cell wall binding motifs. PlyCYU exhibited bactericidal activity against Streptococcus agalactiae, [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมNov
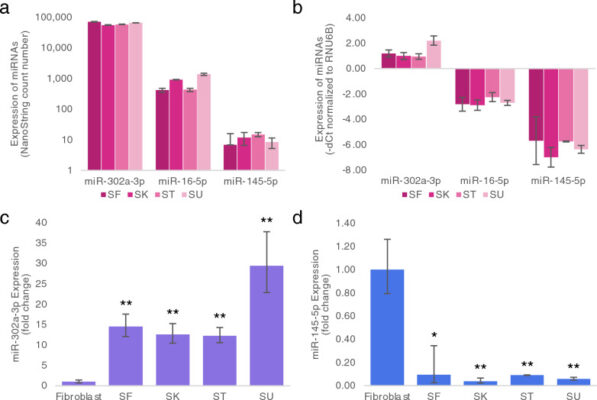
MicroRNA profiles of four induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from distinct tissues
Abstract Objective: Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are generated from a vast number of adult cell types. While they all acquired embryonic stem cell (ESC)-like properties during reprogramming, differences in certain characteristics, including differentiation potential, remained. These differences are hypothesized to be due to epigenetic memory or individual genetic background. Results: This study compared microRNA (miRNA) profiles, which is one [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมNov
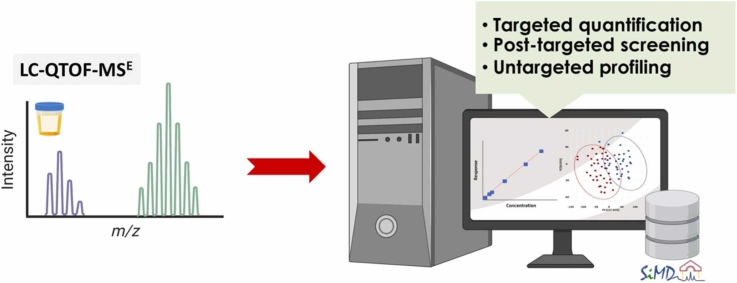
LC-QTOF-MSE with MS1-based precursor ion quantification and SiMD-assisted identification enhances human urine metabolite analysis
Abstract This study presents the development and validation of a liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry method with data-independent acquisition (LC-QTOF-MSE) for targeted quantification, post-targeted screening, and untargeted metabolite profiling. Using MS1-based precursor ion quantification, the method demonstrated excellent analytical performance with linearity (R² > 0.99), accuracy (84 %-131 %), and precision (1 %-17 % relative standard deviation (RSD)). Although LC-QTOF‑MSE sensitivity [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมNov
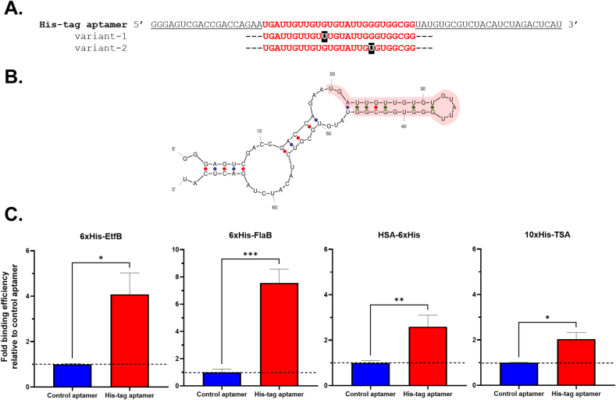
Novel nuclease-resistant RNA aptamer for polyhistidine-tagged proteins and its application in electrochemical aptasensor detection
Abstract The polyhistidine (His) tag is one of the most widely used tags for protein expression, detection, and purification. Aptamers targeting the His tag have been developed for various applications, including western blotting, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation, due to their advantages over His-tag antibodies. However, previously reported His-tag aptamers are either DNA or unmodified RNA, both of which are [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมNov
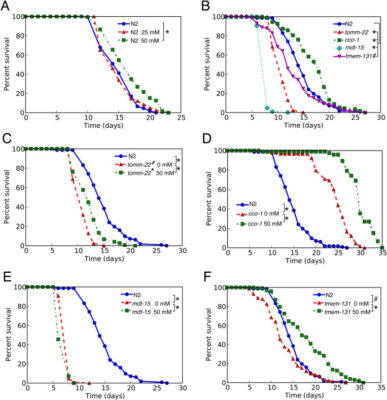
Metformin modulates the unfolded protein responses, altering lifespan and health-promoting effects in UPR-activated worms
Abstract Metformin has been demonstrated to extend lifespan in various model organisms, and its molecular effects are observed in the cytoplasm and multiple organelles, including mitochondria. However, its association with the unfolded protein response (UPR) and its impact on stress resistance and locomotion remain uncertain. In this study, metformin was found to exert differential influences on both UPRmt and UPRer. [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมOct
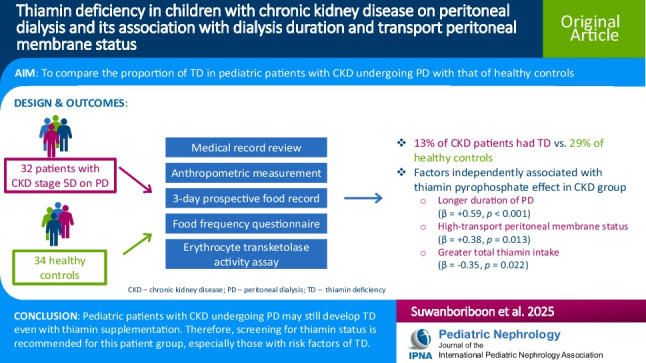
Thiamin deficiency in children with chronic kidney disease on peritoneal dialysis and its association with dialysis duration and transport peritoneal membrane status
Abstract Background: Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) stage 5D receiving peritoneal dialysis (PD) are at risk for thiamin deficiency (TD). This study compared the proportion of TD in pediatric CKD patients undergoing PD with that in healthy controls and evaluated the associations of various factors with TD in CKD patients. Methods: Thirty-two patients with CKD stage 5D and 34 [...]
อ่านเพิ่มเติมOct